“Monetization architecture” refers to the technical and strategic framework that enables a digital product or service (like a SaaS platform, app, or media site) to generate revenue. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its core components:
1. Monetization Model Layer
This layer defines how the product makes money. Common models include:
- Subscription-based: Recurring revenue via tiers (monthly/yearly).
- Pay-per-use: Charges based on usage (e.g., API calls, data processed).
- Freemium: Basic tier for free, advanced features for paid users.
- Advertising: Revenue from ads shown to users (CPM, CPC).
- Marketplace Commission: Take a percentage of each transaction.
- Licensing or White-labeling: Sell technology rights to third parties.
2. Billing & Payments Infrastructure
This layer manages revenue collection and compliance, and typically includes:
- Payment Gateway Integration: Stripe, PayPal, Razorpay, etc.
- Subscription Management: Tools like Chargebee or Stripe Billing to handle trials, upgrades, downgrades, renewals, and dunning.
- Tax Compliance: Systems to manage VAT, GST, or local tax rules.
- Invoice Generation: Automated invoice dispatch and reconciliation.
3. Access Control & Entitlements
Defines what features are available to a user based on their plan or usage:
- Feature Flagging: Tools like LaunchDarkly to enable/disable features.
- Plan-Based Restrictions: Logic to restrict access (e.g., user seats, limits).
- Rate Limiting: Especially in API products to throttle based on plan.
- Dynamic Configuration: Entitlements stored in databases and checked at runtime.
4. Usage Tracking & Metering
Critical for billing accuracy and analytics:
- Events Pipeline: Services (like Segment, Snowplow) to track user events.
- Metering Services: Collect usage data (e.g., data processed, API hits).
- Storage: Usage logs are typically stored in time-series DBs or warehouses (e.g., BigQuery, Snowflake).
5. Reporting & Analytics
To support revenue operations and customer insight:
- Customer Dashboard: Usage stats, billing history, current plan info.
- Admin Tools: Revenue dashboards, customer billing events, churn insights.
- A/B Testing: Measure impact of pricing or feature changes.
6. Experimentation & Pricing Logic
Supports dynamic pricing, discounts, trials:
- Promo Code Systems: Apply discounts or referral bonuses.
- Pricing Service: A microservice to expose price calculation logic.
- Trial Expiry Automation: Handlers to convert, notify, or downgrade users.
7. Compliance, Security & Auditing
To meet regulatory requirements and maintain trust:
- PCI DSS Compliance: Secure payment handling.
- Audit Logging: Track user billing-related actions for support/legal.
- GDPR/CCPA Compliance: Handle user data rights.
Architecture Pattern Example
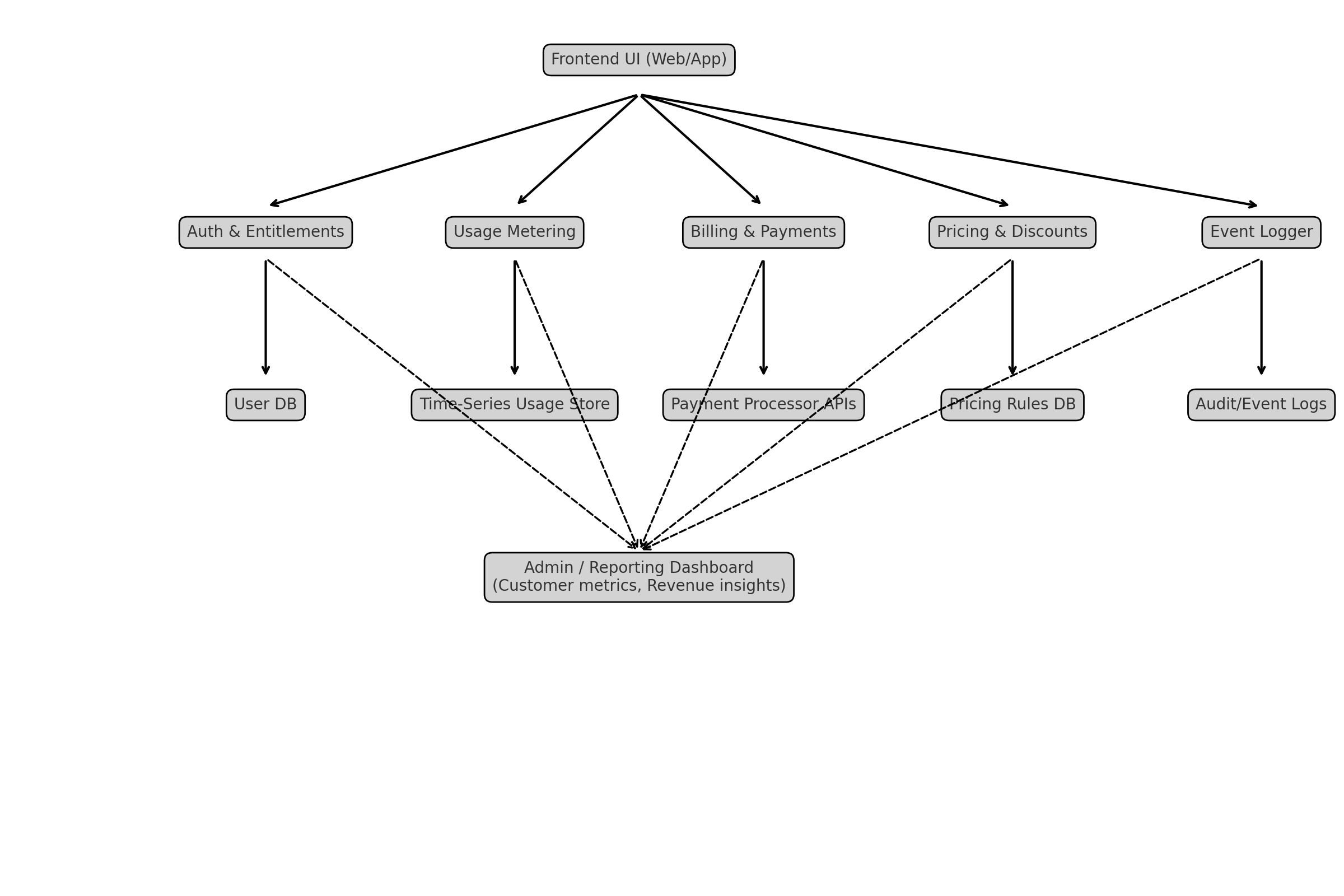
The diagram above illustrates the complete monetization architecture flow, showing how different components interact from the Frontend UI down to the various backend services and data stores. Each service has specific responsibilities:
- Auth & Entitlements: Manages user authentication and feature access control based on subscription plans
- Usage Metering: Tracks and measures user activity for accurate billing and analytics
- Billing & Payments: Handles payment processing, subscription management, and invoice generation
- Pricing & Discounts: Manages dynamic pricing rules, promotional offers, and discount calculations
- Event Logger: Captures comprehensive audit trails and user interaction logs
All these services feed data into the Admin/Reporting Dashboard, providing comprehensive customer metrics, revenue insights, and business intelligence for informed decision-making.